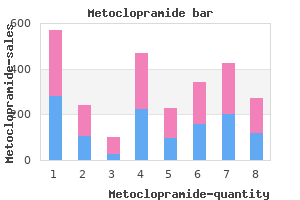
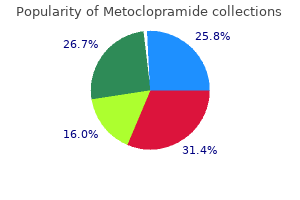
Metoclopramide
"Generic 10 mg metoclopramide otc, gastritis icd 9."
By: Neal H Cohen, MD, MS, MPH
- Professor, Department of Anesthesia and Perioperative Care, University of California, San Francisco, School of Medicine, San Francisco, California

https://profiles.ucsf.edu/neal.cohen
It may be associated with trisomy 21 gastritis neck pain purchase 10 mg metoclopramide mastercard, colonic and ileal atresias syarat diet gastritis buy 10 mg metoclopramide, congenital heart disease gastritis peanut butter buy generic metoclopramide 10 mg on line, genitourinary abnormalities gastritis hiccups buy 10 mg metoclopramide with mastercard, and neurofibromatosis type I. The liver shows increased periportal fibrosis and an increased number of bile ducts that are serpiginous. This lesion is an accentuation of Meyenburg plexus and may progress to congenital hepatic fibrosis with portal hypertension. Caroli disease is a severe form in the spectrum of congenital hepatic fibrosis with cystic dilatation of extrabiliary ducts. The bile ducts in the porta hepatis may have lumina of sufficient diameter (300 µm) to surgically attempt reestablishment of bile flow by portoenterostomy. Initially, the lesion in the liver appears to be a neonatal giant cell hepatitis that progresses to fibrosis and ultimately to biliary cirrhosis. It may progress to cirrhosis of the liver with associated atresia or stenosis of the biliary tree. The cyst wall is 12 mm thick and bile stained and is composed of dense fibrous tissue containing a few inflammatory cells. Paucity of bile ducts is present when fewer than 40% of the portal areas contain sufficient numbers of bile ducts. In Alagille syndrome, the facies are characteristic with a broad forehead, deep-seated eyes, and a saddle nose. The thoracic vertebrae have a butterfly appearance and the portal areas show a deficiency of bile ducts. Viscous secretions obstruct acini and ducts, and high luminal pressure from obstructing secretions in turn causes flattening and atrophy of epithelial cells and progressive dilatation of acini and ducts. Eventually acinar destruction and leakage of proteolytic enzymes into the parenchyma result in fibrosis. Heterotopic Pancreas Nodules of grossly apparent pancreatic tissue isolated from the main body of the pancreas are common incidental findings, usually in the wall of the stomach or proximal small intestine (Figure 18. Most commonly, they appear as small tan nodules on the serosal surface, but they may be intramural and, if so, are usually sessile submucosal masses projecting into the lumen. Heterotopic pancreatic tissue also is seen in Meckel diverticulum, liver, spleen, gastric wall, mesentery, umbilicus, and other remote sites. Annular Pancreas Annular pancreas is due to abnormalities in the migration of the embryonic ventral pancreas, which may result in a ring of pancreatic tissue completely encircling the duodenum (Figure 18. Schwachman-Diamond syndrome is an autosomal recessive condition that occurs in early infancy and is characterized by growth retardation, steatorrhea, and frequent foul-smelling stools. The image should be obtained in a plane perpendicular to creatic islets are increased in size and number and contain prethe major axis of the spine and should include the stomach dominantely insulin-secreting cells. The image should not include cross sections of the heart, kidneys, bladder, or umbilical cord insertion into the abdomen. The image is best localized by aligning the transducer with the spinal column, rotating the transducer 90 and sliding the transducer cephalad or caudad to obtain a scanning plane inferior to the heart and superior to the renal poles. Is the stomach bubble present, normal in size, and situated on the left of the abdomen? Absent stomach bubble suggests tracheo-esophageal abnormalities and an abnormal swallowing mechanism a. Esophageal atresia is associated with trisomy 21; trisomy 18; and cardiac, gastrointestinal, and genito-urinary abnormalities 2. Right-sided stomach bubble suggests possible situs inversus or complete transposition (depending on cardiac situs) 3. A double bubble sign suggests duodenal atresia and is strongly associated with trisomy 21 5. Suggests esophageal atresia, congenital diaphragmatic hernia, situs inversus, and neurologic or musculoskeletal conditions that might affect swallowing 2. Results from abnormal division of the primitive foregut into the trachea and esophagus during the 3rd through 8th weeks of embryonic life c. Should be suspected if polyhydramnios develops and the stomach bubble cannot be identified. In 10% of cases, an associated tracheoesophageal fistula may allow filling of the stomach, or gastric secretions may be present in sufficient quantity to distend the stomach and allow its visualization.
It is believed that even frac tures exposing dentin in primary teeth have no deleterious All films taken should clearly show the apical areas of traumatized teeth (see Figure 1 8- 1 5 gastritis icd 10 discount 10mg metoclopramide with amex, C) gastritis duodenitis diet buy metoclopramide 10 mg on line. In cases in which root fractures are suspected gastritis diet using frozen order metoclopramide 10mg on-line, a second or third radiograph should be made from slightly different angles both vertically f racture diet for gastritis and duodenitis purchase 10mg metoclopramide amex. Various methods have been suggested to restore the fractured crown, including use of strip crowns, pre of larger fractures, treatment is often indicated to restore effect on the pulp and need not be covered. In the case 220 Cellception to Age Three formed aesthetic crowns, and open-faced steel crowns (see Chapter 21). The exposed dentin should be carefully examined to ensure that there is no exposure of the If it is decided to avoid crown restoration, possibly due to a radiograph of the lip should be obtained to rule out the in the soft tissue (see 1 5-9). Late complications, such as coronal discolor ation (see later), usually are attributed not to the fractured crown but to overlooked minor displacement of the tooth and obstruction of blood supply to the pu1p. If the pulp horn is exposed at its incisal edge it may not bleed and therefore may go unnoticed. Several treatment options are available for crown fracture with pu1p exposure in primary teeth, including pulpotomy, root canal treatment, and extraction. The vitality of the tissue and the time elapsed since the injury dictates the treat ment of choice. If the pulp tissue is vital, a cervical pulpot omy suggest that a partial pulpotomy technique is indicated to preserve pulp vitality in a young primary tooth with a wide open apex and thin root dentin wallS. Pulpot omy is the suggested treatment for such exposures with sub sequent aesthetic reconstruction of the crown. If the fracture goes deep into the alveolus, creating a periodontal pocket in the space previously occupied by the loose fragment, both fragments should be extracted. Both fragments may remain close to each other, with the tooth presenting slight mobility and sensitivity to percussion (see Figure be performed (see Chapter 22). If the coronal fragment is pushed away from the apical part of the root, it frequently assumes a lingual inclination that may interfere with the occlusion unless the child has an and no treatment rendered. The unavoidable outcome is a necrotic and infected pulp with consequent swelling or fistula. If massive external inflammatory root resorption is detected or if the follicle of the underlying permanent tooth bud is involved in the inflammatory process, the tooth must be extracted as soon as possible. Leaving such teeth untreated increases the risk of damage to the permanent incisor. If there is no evidence of inflammatory external root resorp tion, some clinicians attempt to save these teeth with com plete pulpectomies. The principle of this treatment is complete removal of the necrotic pulp, filling the pulp canal with a resorbable paste, and providing aesthetic restoration of the crown. Attempts to remove the apical fragment should be avoided as such action may harm the developing permanent successor. These apical fragments usually resorb as part of the physiologic process of tooth replacement. Unlike permanent teeth there is no intention to cause repair of the fracture with calcified tissue in root fractured primary teeth; thus immobilization of the tooth is An injury to the chin may produce a sudden forceful closure 22. Splinting the tooth is recommended orily to alleviate sensitivity during routine function. Parents, if questioned, may recall the injury when a late complication develops, such as tooth discoloration (see "Coronal Discoloration"). These fracture of the mandible may occur mainly in the symphysis, mental, and subcondylar areas1S (Figure fractures. If the fracture is large or extends below the exposed dentin in fractured posterior teeth increases the risk of pulp irritation and may become carious. Clinically, the tooth may disappear com pletely into the surrounding tissues, or the incisal part may remain visible with its clinical crown shorter than an adja cent nontraumatized tooth. Percussion of an intruded tooth produces a metallic sound and does not provoke pain. The root of the primary incisor is normally close to the labial surface of the permanent tooth. If the root of the primary tooth is pushed against the crown of the permanent incisor, it may severely damage the developing tooth bud. Immediate removal of the primary tooth may relieve the pressure and minimize the damage. Fortunately, the root apex of maxillary primary incisors has a labial curvature leading the root away from the permanent tooth in more than can therefore be covered by a composite resin if the area of the gum line, a stainless steel crown is preferable.
Buy 10 mg metoclopramide visa. IBS & SEX 8302678577.
The amniotic cavity appears as a space between the cytotrophoblast and the embryoblast bile gastritis diet buy metoclopramide 10 mg without a prescription. The embryoblast differentiates into a bilaminar embryonic disc consisting of epiblast gastritis fiber generic 10 mg metoclopramide with mastercard, related to gastritis symptoms breathing order metoclopramide 10 mg the amniotic cavity gastritis diet �������������� generic metoclopramide 10mg visa, and hypoblast, adjacent to the blastocyst cavity. The prechordal plate develops as a localized thickening of the hypoblast, which indicates the future cranial region of the embryo and the future site of the mouth; the prechordal plate is also an important organizer of the head region. The approximate order of frequency of ectopic implantations is indicated alphabetically (A, most common, H, least common). A, the uterine tube has been surgically removed and sectioned to show the conceptus implanted in the mucous membrane (Г-3). A woman who was sexually assaulted during her fertile period was given large doses of estrogen twice for 1 day to interrupt a possible pregnancy. A 23-year-old woman consulted her physician about severe right lower abdominal pain. A 30-year-old woman had an appendectomy toward the end of her menstrual cycle; 8ВЅ months later, she had a child with a congenital anomaly of the brain. A 42-year-old woman finally became pregnant after many years of trying to conceive. Cessation of menstruation is often the first indication that a woman may be pregnant. Approximately 3 weeks after conception, approximately 5 weeks after the last normal menstrual period. Pregnancy Symptoms Frequent symptoms of pregnancy are nausea and vomiting, which may occur by the end of the third week; however, the time of onset of these symptoms varies. Vaginal bleeding at the expected time of menstruation does not rule out pregnancy because there may be a slight loss of blood from the implantation site of the blastocyst. Implantation bleeding results from leakage of blood into the uterine cavity from disrupted lacunar networks in the implanted blastocyst (see. When this bleeding is interpreted as menstruation, an error occurs in determining the expected date of confinement and delivery date of the baby. Note the surrounding endometrium (E) and secondary umbilical vesicle (yolk sac) (arrow). During gastrulation, the bilaminar embryonic disc is converted into a trilaminar embryonic disc. Extensive cell shape changes, rearrangement, movement, and changes in adhesive properties contribute to the process of gastrulation. Gastrulation is the beginning of morphogenesis (development of body form) and is the significant event occurring during the third week. The first morphologic sign of gastrulation begins with formation of the primitive streak on the surface of the epiblast of the embryonic disc. Each of the three germ layers (ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm) gives rise to specific tissues and organs: Embryonic ectoderm gives rise to the epidermis, central and peripheral nervous systems, the eye, and inner ear, and, as neural crest cells, to many connective tissues of the head (see Chapter 5). Embryonic mesoderm gives rise to all skeletal muscles, blood cells and the lining of blood vessels, all visceral smooth muscular coats, the serosal linings of all body cavities, the ducts and organs of the reproductive and excretory systems, and most of the cardiovascular system. In the trunk, it is the source of all connective tissues, including cartilage, bones, tendons, ligaments, dermis, and stroma of internal organs. Figure 4-2 Illustrations of the formation of the trilaminar embryonic disc (days 15 to 16). The arrows indicate invagination and migration of mesenchymal cells from the primitive streak between the ectoderm and endoderm. C, E, and G, Dorsal views of the embryonic disc early in the third week, exposed by removal of the amnion. The prechordal plate, indicating the head region in C, is indicated by a light blue oval because this thickening of endoderm cannot be seen from the dorsal surface. At the beginning of the third week, an opacity formed by a thickened linear band of epiblast-the primitive streakappears caudally in the median plane of the dorsal aspect of the embryonic disc. The primitive streak results from the proliferation and movement of cells of the epiblast to the median plane of the embryonic disc. As the streak elongates by addition of cells to its caudal end, its cranial end proliferates to form a primitive node. Concurrently, a narrow groove-primitive groove-develops in the primitive streak that is continuous with a small depression in the primitive node-the primitive pit.
Recognize that spoken words Letters Make Words are represented in written language by Picture Story specific sequences of letters gastritis of the antrum metoclopramide 10mg generic. Add or substitute individual sounds (phonemes) in simple gastritis diet 66 cheap 10 mg metoclopramide otc, onesyllable words to chronic gastritis symptoms treatment quality metoclopramide 10 mg make new words gastritis symptoms nausea buy metoclopramide 10 mg visa. Demonstrate basic knowledge of one-to-one letter-sound correspondences by producing the primary or many of the most frequent sounds for each consonant. Associate the long and short sounds with common spellings (graphemes) for the five major vowels. Distinguish between similarly spelled words by identifying the sounds of the letters that differ. Use a combination of drawing, dictating, and writing to compose opinion pieces in which they tell a reader the topic or the name of the book they are writing about and state an opinion or preference about the topic or book. Use a combination of drawing, dictating, and writing to compose informative/explanatory texts in which they name what they are writing about and supply some information about the topic. Use a combination of drawing, dictating, and writing to narrate a single event or several loosely linked events, tell about the events in the order in which they occurred, and provide a reaction to what happened. With guidance and support, orally respond to questions and suggestions from adults and peers and add details to strengthen writing as needed. With guidance and support from adults and peers, explore a variety of digital tools in participating in a production of a published writing. Waterford provides access to a word processor feature for producing and publishing writing. With guidance and support from adults, recall information from experiences or gather information from provided sources to answer a question. Participate in collaborative conversations with diverse partners about kindergarten topics and texts with peers and adults in small and larger groups. Waterford contains many teacher materials that can be used to integrate speaking and listening into classroom activities. Confirm understanding of a text read aloud or information presented orally or through other media by asking and answering questions about key details and requesting clarification if something is not understood. Ask and answer questions in order to seek help, get information, or clarify something that is not understood. Describe familiar people, places, things, and events and, with prompting and support, provide additional details. Add drawings or other visual displays to descriptions as desired to provide additional detail. Demonstrate command of the conventions of Standard English grammar and usage when writing or speaking. Demonstrate command of the conventions of standard English capitalization, punctuation, and spelling when writing. Spell simple words phonetically, drawing on knowledge of sound-letter relationships. Determine or clarify the meaning of unknown and multiplemeaning words and phrases based on kindergarten reading and content. With guidance and support from adults, explore word relationships and nuances in word meanings. Demonstrate understanding of frequently occurring verbs and adjectives by relating them to their opposites (antonyms). Use words and phrases acquired All activities in Speaking and Listening and Language through conversations, reading and standards provide opportunities for students to use words being read to, and responding to texts. Identify words and phrases in stories or poems that suggest feelings or appeal to the senses. Explain major differences between books that tell stories and books that give information, drawing on a wide reading of a range of text types. Use illustrations and details in a story to describe its characters, setting, or events. With prompting and support, read prose and poetry of appropriate complexity for grade 1. Describe the connection between two individuals, events, ideas, or pieces of information in a text. When bolded words are clicked, students hear a slowed pronunciation and definition in a pop-up with an illustration. Ask and answer questions to help determine or clarify the meaning of words and phrases in a text.
References:
- https://foreonline.org/wp-content/uploads/2016/11/2.-Ahmad_2016-BSM-physical-exam-elbow.pdf
- http://www.fao.org/3/y5394e/y5394e.pdf
- https://www.honorhealth.com/sites/default/files/documents/medical-services/honorhealth-therapeutic-breast-massage.pdf