DDAVP
"Purchase ddavp 10mcg with amex, diabetes research institute miami."
By: Jeanine P. Wiener-Kronish, MD
- Anesthetist-in-Chief, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts
Nitric oxide/cyclic guanosine monophosphate signalling mediates an inhibitory action on sensory pathways of the micturition reflex in the rat diabetes mellitus definition nhs ddavp 10 mcg fast delivery. Patient-selected goals in overactive bladder: a placebo controlled randomized double-blind trial of transdermaloxybutynin for the treatment of urgency and urge incontinence diabetes vinegar order ddavp 10 mcg otc. Pharmacological activities of the main metabolite of flavoxate 3-methylflavone-8-carboxylic acid quest diagnostics diabetes test trusted ddavp 10mcg. A comparison of the effects on saliva output of oxybutynin chloride and tolterodine tartrate blood sugar levels normal quality 10mcg ddavp. Beneficial effect of intranasal desmopressin for men with benign prostatic hyperplasia and nocturia: preliminary results. Treatment of overactive bladder: selective use of anticholinergic agents with low drug-drug interaction potential. Obesity is associated with a more severe overactive bladder disease state that is effectively treated with oncedaily administration of trospium chloride extended release. OnabotulinumtoxinA improves quality of life in patients with neurogenic detrusor overactivity. Bloodbrain barrier permeation and efflux exclusion of anticholinergics used in the treatment of overactive bladder. Solifenacin appears effective and well tolerated in patients with symptomatic idiopathic detrusor overactivity in a placebo- and tolterodine-controlled phase 2 dosefinding study. Long-term darifenacin treatment for overactive bladder in patients aged 65 years and older: analysis of results from a 2-year, open-label extension study. Randomized double-blind, active-controlled phase 3 study to assess 12-month safety and efficacy of mirabegron, a (3)-adrenoceptor agonist, in overactive bladder. The effects of antimuscarinic treatments in overactive bladder: a systematic review and meta-analysis. The effects of antimuscarinic treatments in overactive bladder: an update of a systematic review and meta-analysis. Silodosin therapy for lower urinary tract symptoms in men with suspected benign prostatic hyperplasia: results of an international, randomized, double-blind, placebo- and active-controlled clinical trial performed in Europe. Doubleblind, placebo-controlled, cross-over study of flavoxate in the treatment of idiopathic detrusor instability. Randomized, double-blind placebo- and tolterodine-controlled trial of the oncedaily antimuscarinic agent solifenacin in patients with symptomatic overactive bladder. OnabotulinumtoxinA 100 U significantly improves all idiopathic overactive bladder symptoms and quality of life in patients with overactive bladder and urinary incontinence: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Clinical efficacy, safety, and tolerability of once-daily fesoterodine in subjects with overactive bladder. Transient receptor potential vanilloid subfamily 1 is essential for the generation of noxious bladder input and bladder overactivity in cystitis. European Urology Supplements, Volume 11, Issue 1, February 2012a, Page e366 Charrua A. European Urology Supplements, Volume 11, Issue 1, February 2012b, Page e366 Charrua A, Matos R, Marczylo T, Nagy I, Cruz F. European Urology Supplements 15(3):e274-e274a March 2016 Chartier-Kastler E, Denys P, Kepenne V, et al. Efficacy and safety of onabotulinumtoxinA 100 U for treatment of urinary incontinence due to neurogenic detrusor overactivity in non-cathetersing multiple sclerosis patients. Muscarinic receptors of the urinary bladder: detrusor, urothelial and prejunctional. The minor population of M3-receptors mediate contraction of human detrusor muscle in vitro. Botulinum toxin type A improves benign prostatic hyperplasia symptoms in patients with small prostate. Sustained beneficial effects of intraprostatic botulinum toxin type A on lower urinary tract symptoms and quality of life in men with benign prostatic hyperplasia.
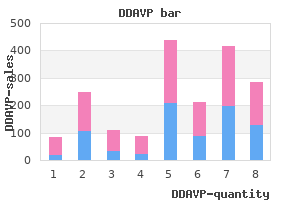
Numbers for dosages must be clear and unambiguous take particular care over 4s and 9s diabetes zentrum wiesbaden purchase ddavp 10 mcg amex, for example diabetes warning signs discount 10mcg ddavp amex. If the use is necessary diabetes symptoms videos 10mcg ddavp amex, the decimal point must be precisely marked and diabetic diet what to avoid buy 10mcg ddavp amex, if appropriate, preceded by a zero (0). The weights for all children must be recorded on the drug chart in Kg (the policy only asks for children<12yrs). Ensure that changes to the drugs are communicated to the nursing staff (and patient/parents/carers if appropriate. Common potential interactions are: Drug Carvedilol Ciclosporin Clopidogrel Interacts with Flecainide Digoxin Macrolide antibiotics Proton pump inhibitors Amiodarone Macrolides Digoxin Carvedilol Bosentan Amiodarone Warfarin Antibiotics Bosentan Comment Reduce flecainide doses by at least 30%, check levels Reduce digoxin dose by at least 30%, check levels Avoid use, or check ciclosporin levels these cause reduced anti-platelet effect Reduce digoxin dose by at least 30%, check levels Avoid use, or reduce digoxin dose by at least 30%, check levels if to be used long-term Reduce digoxin dose by at least 30%, check levels Causes lowering of digoxin levels, but not enough to be clinically significant. Indications Paediatric cardiology patients (both pre and post operative) with a significant left to right shunt that requires additional intervention above diuretic therapy. Primary systemic hypertension following thorough investigation of possible aetiology and in absence of renal disease structural or functional. There is also some cross reactivity on the bradykinin system as well as possible direct effects on cardiac reverse-remodelling. Available preparations Captopril: Licensed liquids available in 2 different strengths (Noyada; 21 day expiry): 5mg/5ml to be used for doses <2. The decision to commence captopril should be taken by the admitting consultant paediatric cardiologist or paediatrician with an interest under the direction of the consultant paediatric cardiologist. Day case admission this should be arranged by the consultant paediatric cardiologist via their secretary and the ward sister. This will be a full day admission and patients should ideally arrive by 09:00am on the day of admission. Prior to admission, all patients should have an echocardiogram (Echo) performed within 6 weeks of admission. Identify appropriate physiological parameters with medical staff, and record on age appropriate observation chart. The test dose can be given prior to blood results being available unless there is reason to suspect renal dysfunction. However, if symptoms persist and treatment required, patient should be laid flat, legs elevated and a fluid bolus considered. Depending on the preference of the admitting cardiologist this dose should be escalated in time to 0. Up-titration of the dose should be done with caution in unstable or young patients, usually under inpatient supervision with careful monitoring of renal function/electrolytes. Once patient has reached desired dose they should be discharged with a completed discharge letter with new dose prescribed for the G. Further increases can be managed either as an outpatient or a subsequent admission. However, prior to discharge it should be assessed, whether the patient can tolerate administration of the diuretics with the captopril at the same time, without causing significant hypotension. Conversion to either enalapril or lisinopril should only be undertaken when the patient has been proven to tolerate captopril trial. Contributors: Network Medicines Group guideline created 2019 7. Alternatives to losartan in older patients are valsartan or candesartan (licensed indications: hypertension and/or heart failure). Doses of up to 4 mg/kg/day have been given in cases of Marfan syndrome with severe aortopathy. If central venous access is not available, use a large peripheral vein and monitor the injection site closely. Concentrations exceeding amiodarone 2mg in 1mL should always be given via a central venous access device except in extreme clinical emergency. Incompatiblities Aminophyllin, furosemide, heparin, potassium acid phosphate, phosphate infusions, sodium bicarbonate, sodium chloride, sodium nitroprusside.
Displacement and recovery of the vesical neck position during pregnancy and after childbirth diabete infantil buy ddavp 10mcg on line. Direction sensitive sensor probe for the evaluation of voluntary and reflex pelvic floor contractions diabetes medications starting with l generic ddavp 10mcg line. Vaginal high-pressure zone assessed by dynamic 3-dimensional ultrasound images of the pelvic floor diabetes type 1 breakfast ideas generic 10 mcg ddavp with amex. Diagnosing pubovisceral avulsions: a systematic review of the clinical relevance of a prevalent anatomical defect managing diabetes 911 purchase 10 mcg ddavp with amex. Simу Gonzбlez M, Cassadу Garriga J, Dosouto Capel C, Porta Roda O, Perellу Capу J, Gich Saladich I. Is obsteric anal sphincter injury a risk factor for levator ani muscle avulsion in vaginal delivery? The assessment of levator trauma: a comparison between palpation and 4D pelvic floor ultrasound. Do ultrasound findings of levator ani "avulsion" correlate with anatomical findings: A multicenter cadaveric study. Pelvic floor function in nulliparous women using three-dimensional ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging. Interobserver repeatability of three- and four-dimensional ultrasound assessment of pelvic floor muscle anatomy and function. Interobserver and interdisciplinary reproducibility of 3D endovaginal ultrasound assessment of pelvic floor anatomy. Visualization of the endopelvic fascia by transrectal three-dimensional ultrasound. Use of 3D ultrasound as a new approach to assess obstetrical trauma to the pelvic floor. Three-dimensional ultrasound imaging of the pelvic floor: the effect of parturition on paravaginal support structures. Paravaginal defects: a comparison of clinical examination and 2D/3D ultrasound imaging. Levator avulsion using a tomographic ultrasound and magnetic resonance-based model. Tomographic ultrasound imaging of the pelvic floor in nulliparous pregnant women: limits of normality. Translabial three-dimensional ultrasonography compared with magnetic resonance imaging in detecting levator ani defects. Accuracy of assessing pelvic organ prolapse quantification points using dynamic 2D transperineal ultrasound in women with pelvic organ prolapse. Diagnosis of posterior enterocele: comparison of rectal ultrasonography with intraoperative diagnosis. Posterior pelvic floor disorders: a prospective comparison using introital ultrasound and colpocystodefecography. Posterior compartment prolapse on two-dimensional and threedimensional pelvic floor ultrasound: the distinction between true rectocele, perineal hypermobility and enterocele. Brusciano L, Limongelli P, Pescatori M, Napolitano V, Gagliardi G, Maffettone V, et al. Anterior but not posterior compartment prolapse is associated with levator hiatus area: a three- and four-dimensional transperineal ultrasound study. Dynamic anal endosonography may challenge defecography for assessing dynamic anorectal disorders: results of a prospective pilot study. Evaluation of established and new reference lines for the standardization of transperineal ultrasound. Ultrasound assessment of pelvic organ prolapse: the relationship between prolapse severity and symptoms. Costantini S, Esposito F, Nadalini C, Lijoi D, Morano S, Lantieri P, Mistrangelo E. Ultrasound imaging of the female perineum: the effect of vaginal delivery on pelvic floor dynamics. Prevalence of bladder neck mobility in asymptomatic non-pregnant nulliparous volunteers. The prevalence of major abnormalities in the levator ani in urogynaecological patients. Pubococcygeus-puborectalis trauma after forceps delivery: evaluation of the levator ani muscle with 3D/4D ultrasound.
Syndromes
- Airway obstruction -- can lead to death
- Enlarged (dilated) pupils
- Children in day-care
- Counting carbohydrates
- Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration - www.samhsa.gov
- Diabetes insipidus - renal
- Blood in the vomit (looks bright red, or brown like coffee-grounds)
- Occurs when you are lying flat
Do cystometric findings predict the results of intravesical hyaluronic acid in women with interstitial cystitis? An assessment of the use of intravesical potassium in the diagnosis of interstitial cystitis diabetes diet weekly menu 10 mcg ddavp visa. The role of urinary potassium in the pathogenesis and diagnosis of interstitial cystitis diabetic breakfast buy generic ddavp 10 mcg. Intravesical potassium chloride sensitivity test in men with chronic pelvic pain syndrome diabetes warning signs type 2 discount 10mcg ddavp amex. The overlap of interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome and overactive bladder diabetes symptoms type 2 diabetes cheap ddavp 10 mcg. Abnormal sensitivity to intravesical potassium in interstitial cystitis and radiation cystitis. The prevalence of interstitial cystitis in gynecologic patients with pelvic pain, as detected by intravesical potassium sensitivity. Prevalence of positive potassium sensitivity test which is an indicator of bladder epithelial permeability dysfunction in a fixed group of turkish women. Does the potassium stimulation test predict cystometric, cystoscopic outcome in interstitial cystitis? Urodynamic study and potassium sensitivity test for women with frequency-urgency syndrome and interstitial cystitis. Interstitial cystitis versus detrusor overactivity: A comparative, randomized, controlled study of cystometry using saline and 0. The interstitial cystitis data base study: Concepts and preliminary baseline descriptive statistics. Glomerulations in women with urethral sphincter deficiency: Report of 2 cases [corrected]. Cystoscopic findings consistent with interstitial cystitis in normal women undergoing tubal ligation. Toward a precise definition of interstitial cystitis: Further evidence of differences in classic and nonulcer disease. Are patient symptoms predictive of the diagnostic and/or therapeutic value of hydrodistention? Symptoms and cystoscopic findings in patients with untreated interstitial cystitis. Bladder necrosis following hydrodistention in patients with interstitial cystitis. Decreased 3h-thymidine incorporation by human bladder epithelial cells following exposure to urine from interstitial cystitis patients. An antiproliferative factor from interstitial cystitis patients is a frizzled 8 protein-related sialoglycopeptide. Antiproliferative activity is present in bladder but not renal pelvic urine from interstitial cystitis patients. Bladder stretch alters urinary heparin-binding epidermal growth factor and antiproliferative factor in patients with interstitial cystitis. Changes in urine markers and symptoms after bladder distention for interstitial cystitis. Antiproliferative factor, heparin-binding epidermal growth factor-like growth factor, and epidermal growth factor: Sensitive and specific urine markers for interstitial cystitis. Antiproliferative factor, heparin-binding epidermal growth factor-like growth factor, and epidermal growth factor in men with interstitial cystitis versus chronic pelvic pain syndrome. Concentrations of specific epithelial growth factors in the urine of interstitial cystitis patients and controls. Sensitivity and specificity of antiproliferative factor, heparinbinding epidermal growth factor-like growth factor, and epidermal growth factor as urine markers for interstitial cystitis. Prevalence and incidence of chronic pelvic pain in primary care: Evidence from a national general practice database. Interstitial cystitis and chronic pelvic pain: New insights in neuropathology, diagnosis, and treatment.
Order 10mcg ddavp otc. Diabetes symptoms in marathi / मधूमेहाची लागण होण्यापूर्वीची महत्त्वाची ८ लक्षणे.
References:
- https://bmcbiol.biomedcentral.com/track/pdf/10.1186/s12915-015-0201-x.pdf
- http://status.neticrm.tw/Severe-Spondylolisthesis-Pathology-Diagnosis-Therapy.pdf
- https://omavofe.files.wordpress.com/2015/06/pathophysiology-of-lumbar-spondylosis-pdf.pdf
- https://www.merseycare.nhs.uk/media/3275/sa28-v4-legionella-policy-uploaded-20jan-17-rev-dec-19.pdf
- https://www.acns.org/UserFiles/file/Guideline_Twelve__Guidelines_for_Long_Term.8.pdf